Palmyra Fruit (Ice Apple): Taste, Uses & Regional Names

Palmyra Fruit (Ice Apple): Taste, Uses & Regional Names
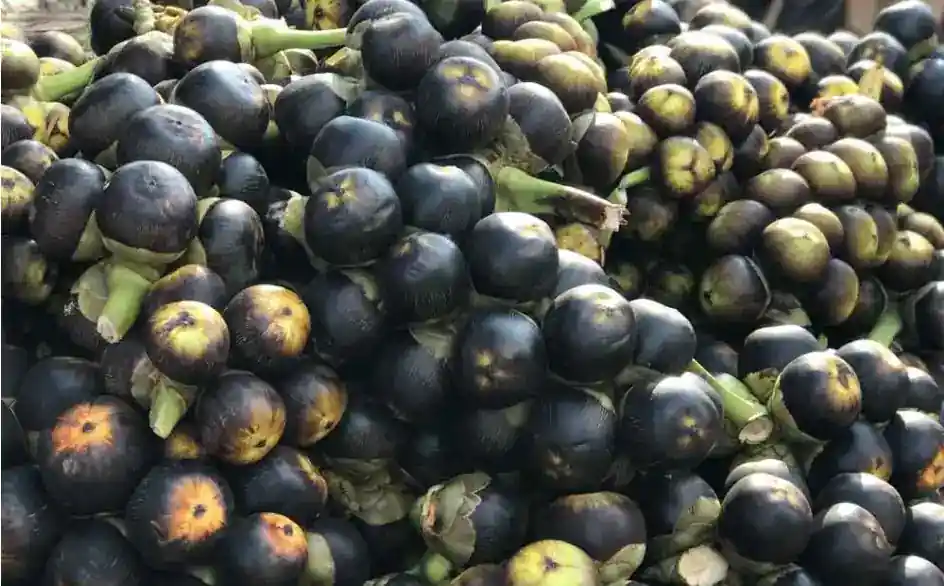
The palmyra fruit, also known as ice apple, is a large fruit (10-18 cm diameter) with a black husk, growing in clusters. It is unique in that both its unripe seeds and the ripe fruit are edible.
Characteristics & Consumption:
- Unripe Seeds: The top is cut to reveal sweet, translucent, pale-white jelly seed sockets (2-4 per fruit), similar to lychee but milder and without a pit. These inspired the Bengali sweet "jolbhora."
- Ripe Fruit: The soft, orange-yellow mesocarp pulp is sugary and rich in vitamins A and C. It contains bitter compounds called flabelliferrins.
- Ripe Husk: If left to ripen, the fibrous outer layer turns purplish-black and tastes like coconut. The skin is also edible.
- Bengali Cuisine: The viscous fluid from ripe fruit is used in sweet dishes like "taler bora" (palmyra vadas) and "tal-khir" (palmyra kheer).
- Thai Cuisine: Used to make a steamed fluffy cake called "Khanom Tan."
Regional Names:
The fruit is known by various names across India and Southeast Asia, including:
- Hindi-Urdu: Taad Gola (ताड़ गोला / تاڑ گولا)
- Malayalam: Nonku (നൊങ്ക്)
- Tamil: Nungu (நுங்கு)
- Odia: Tala (ତାଳ)
- Indonesian: Buah Lontar or Siwalan (Ice apple)
- Kannada: Taati Nungu / Taati Ningu (ತಾಟಿ ನುಂಗು / ತಾಟಿ ನಿಂಗು)
- Burmese: Htan-thee (ထန်းသီး)
- Telugu: Thaati Munjalu (తాటి ముంజలు)
- Tulu: Erolu (ಇರೋಲು)
In summary, the palmyra fruit is a versatile fruit with edible parts at different stages of ripeness, enjoyed in various culinary forms and known by numerous regional names across South and Southeast Asia.